It’s looking a lot more like the Federal Reserve is winning its battle against inflation, but when the latest decision on interest rates is announced Wednesday afternoon, investors should brace themselves for continued tough talk out of the central bank.
The Fed is widely expected to unveil another quarter-point increase in the federal-funds rate at the upcoming meeting.
But beyond the immediate decision, some observers say that instead of the Fed focusing on the improving inflation picture, they’re likely to continue emphasizing keeping interest rates high. That includes the potential for still one more interest-rate increase before the year is out and any discussion about lowering rates is likely to be kept off the table.
It’s not that the Fed won’t acknowledge the significant progress in slowing inflation from a four-decade high, especially in the wake of good news from the June Consumer Price Index report. The issue is that the Fed doesn’t want to send signals that would lead stock and bond investors to get ahead of themselves in expecting a quick turn toward lowering rates in coming months.
"What the Fed effectively has to do is basically say, 'OK, we’re probably going to pause here soon,' but they have to convince the market the next move is just as likely to be up as down," says Tiffany Wilding, a managing director and economist at Pimco.
That, Wilding says, means messaging from the Fed along the lines of "yes, we’ve got some good news on inflation, but we need to see several more inflation reports with good news, or we’re not there yet…and we’re very focused on bringing inflation down."
When it comes to the July meeting, there’s wide agreement that the Fed will raise rates against a backdrop of continued strength in the jobs market and an economy that has defied widespread expectations of falling into a recession.
"We think that another 25-basis-point rate hike in July is as close to a done deal as we can say without saying it’s 100% going to happen," says Wilding. The CME FedWatch Tool, which tracks traders’ bets on the direction of interest rates, puts the chances of a Fed rate hike at 99.8%.
That rate hike would take the fed-funds rate to a 5.25%-5.5% target. This key rate had been at zero before the Fed started raising rates in March 2022.
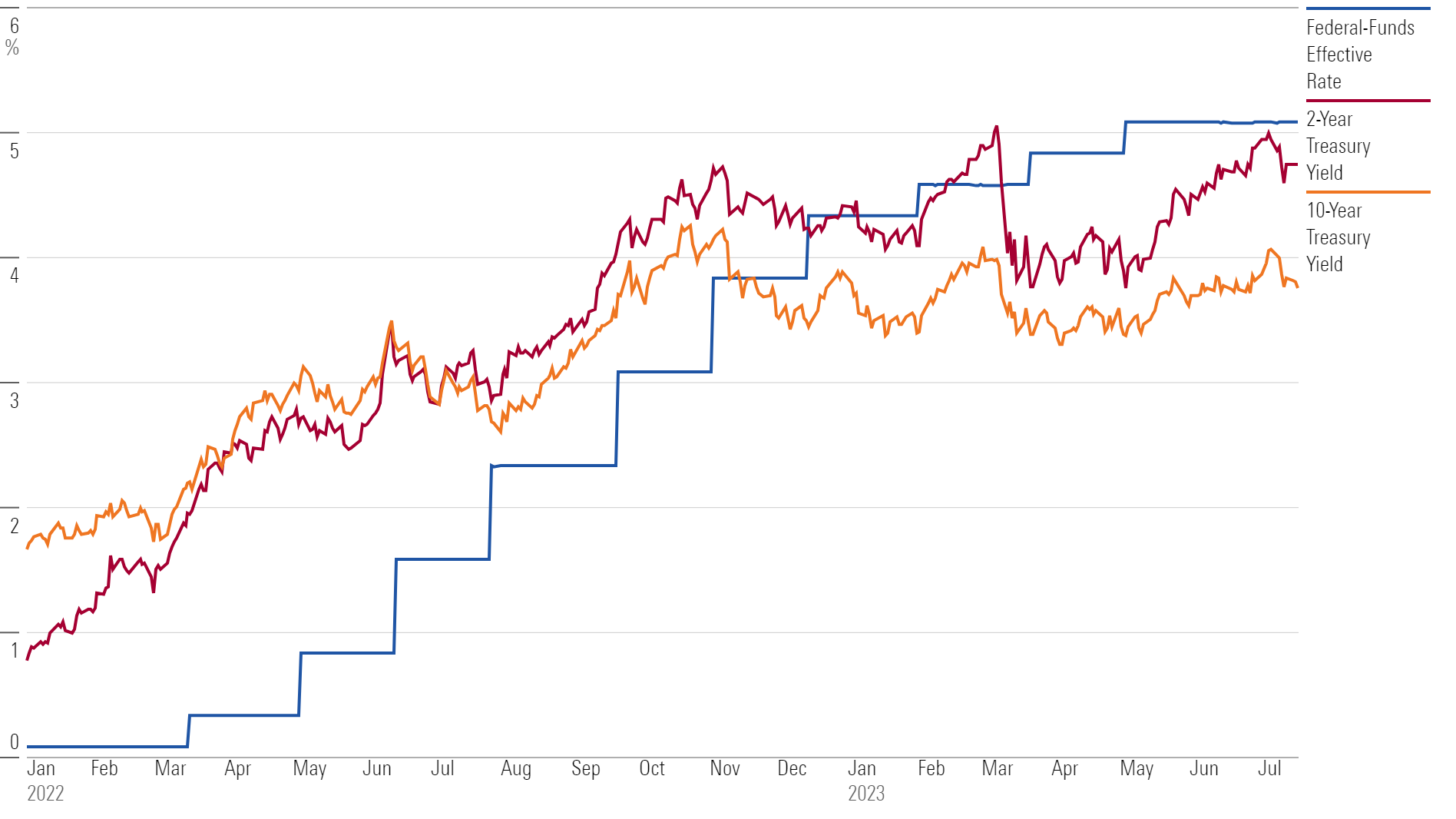
With a July rate increase seen as baked in, the big question is what happens over the course of the next several months.
Matt Brill, head of North America investment-grade credit at Invesco, says it appears likely the Fed will then hold rates steady at its September Federal Open Market Committee meeting, where policy is set. From there, the Fed won’t be meeting again until 31 October and 1 November, which gives officials time to assess whether the improvement in inflation evident in the June CPI is sustained.
Skipping a rate increase in September "gives them enough time to continue to see this trend play out," says Brill.
While Brill believes that the July rate hike will prove to be the final increase in interest rates for this cycle, like Wilding, he thinks the Fed won’t signal it is done.
"They’ll probably state that the work is not done, and that they need to see inflation come down," he says. "I think they will continue to be ultra-hawkish in terms of their rhetoric."
Why Talk Tough if Inflation is Coming Down?
It amounts to what is known in Wall Street jargon as financial conditions.
In order for the Fed to bring down inflation, it needs to slow the economy, and to slow the economy, it needs to tighten financial conditions – make it more costly for businesses and individuals to borrow money and raise capital in general, such as through the stock market. Economists use varying metrics when assessing the restrictiveness of monetary policy, but at its most basic level, it means keeping interest rates high.
The challenge for the Fed is that it can only directly influence the federal-funds rate, which is the rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans. All other interest rates are set by investors in the markets, such as in the government-bond market, or based on market rates.
But the markets are forward-looking, and if investors believe the Fed will be cutting rates, that means bond yields will fall, taking down other rates, such as those on mortgages, making it easier to borrow.
"They will certainly try to talk tough because the last thing they want is for the market to loosen financial conditions so much that it fights against what they want to do," says Kathy Jones, chief fixed income strategist at Charles Schwab.
"The Fed is very, very concerned about the credibility issue" when it comes to their determination to fight inflation, "and very, very concerned about the potential for a rebound in inflation…and that’s a scenario they fear more than they fear overdoing it" and leading the economy into a recession.
In Pimco’s assessment, monetary policy is in restrictive territory. "When we look at our broader financial conditions index […] that has tightened at a faster pace and to a level that we haven’t seen since the 2008 financial crisis," Wilding says.
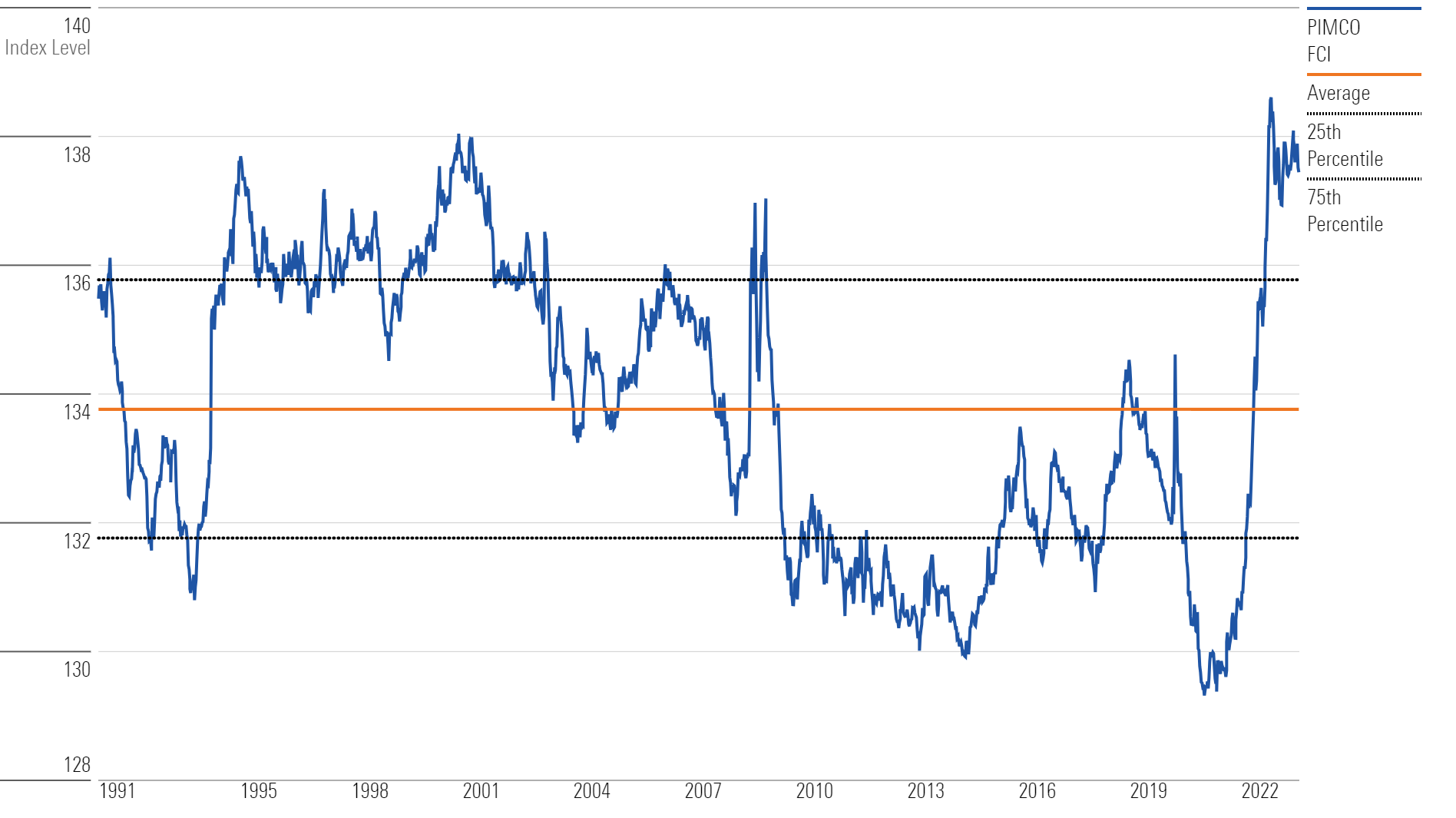
In the firm’s assessment, Wilding says even though there are clear signs of improvement in inflation that suggest the July rate hike may be the last, a tight labor market and sticky wage inflation will require the Fed to keep its foot on the brakes of the economy. That means keeping financial conditions tight.
"If the market brings forward that easing, they might not reach their inflation target because they still need policy to be tight today," says Pimco’s Wilding.
"What the Fed wants to do is keep the broader constellation of financial conditions tight because keeping financial conditions tight today will help slow the economy and then ultimately bring down inflation in the future because monetary policy works through lags."
For the Trading Week Ended 21 July
• The Morningstar US Market Index rose 0.72%;
• The best-performing sectors were energy, up 3.7%, and financial services, up 3.1%;
• The worst-performing sectors were communication services, down 2.1%, and consumer cyclical, down 1.7%;
• Yields on 10-year US Treasuries increased to 3.85% from 3.82%;
• West Texas Intermediate crude prices rose 2.19% to $77.07 per barrel;
• Of the 857 US-listed companies covered by Morningstar, 582, or 68%, were up, and 275, or 32%, were down.
Which Stocks Are Up Right Now?
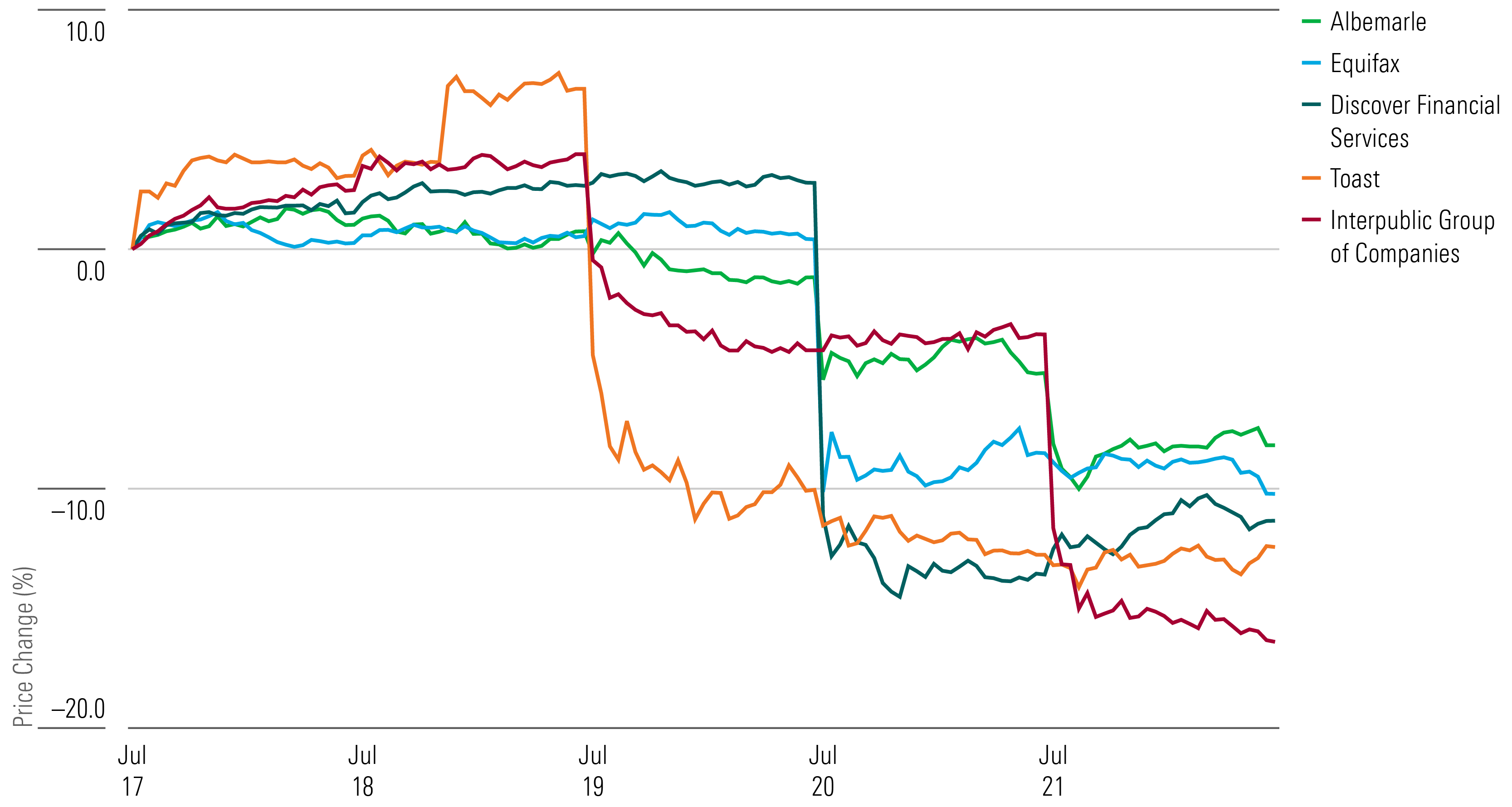
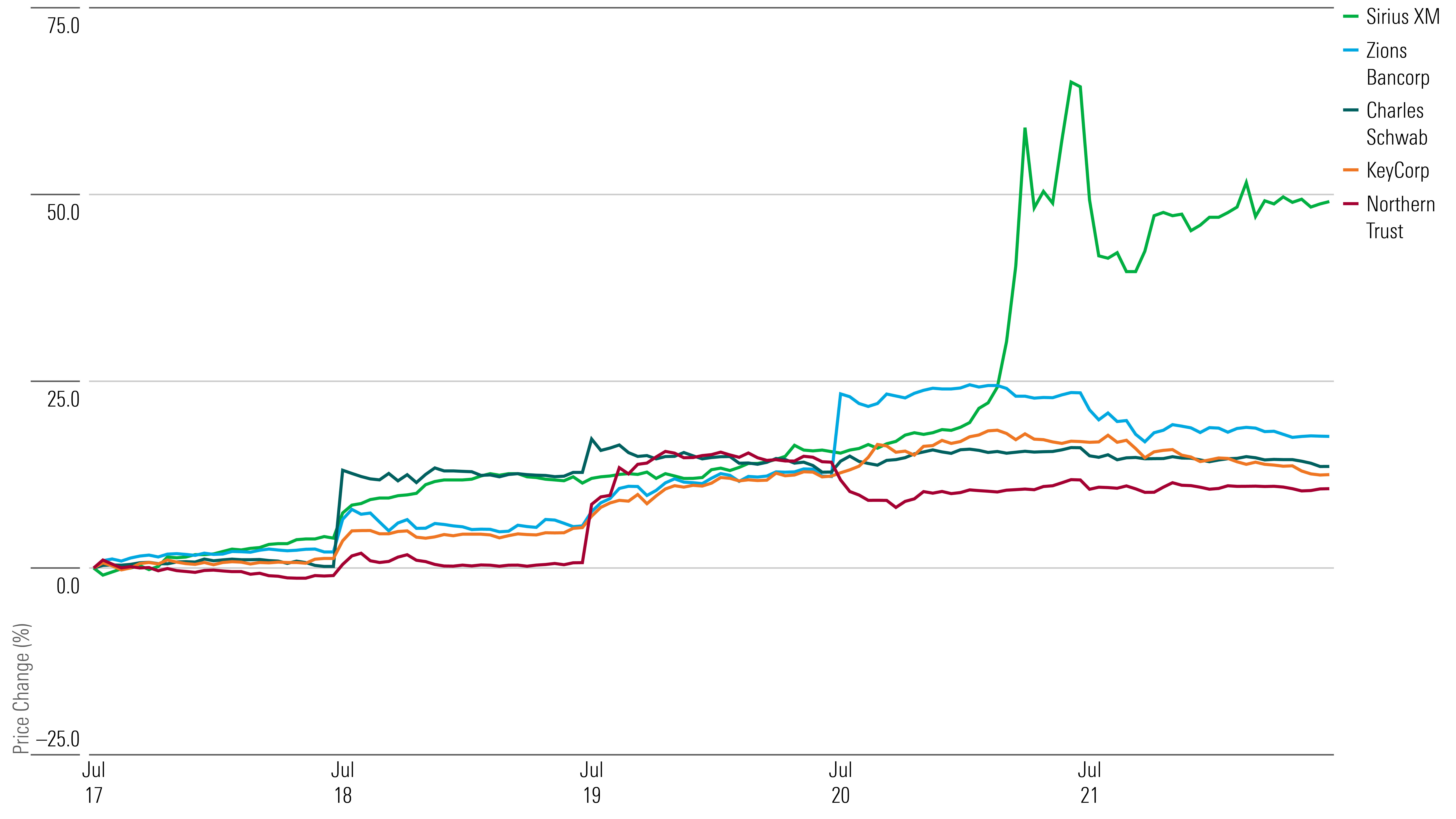
Sirius XM Holdings [SIRI] stock surged over 40%, driven not by company news but rather a short squeeze. Morningstar senior equity analyst Neil Macker says about 34% of the broadcasting company’s shares were held shorted on July 20 as investors attempted to capitalize on the reformulation of Liberty Media tracking stocks, which traditionally traded at a discount of roughly 30%.
With banks kicking off earnings season, shares for regional banks such as Zions Bancorp [ZION] and KeyCorp [KEY] jumped after posting their second-quarter results.
Zions’ earnings per share of $1.11 were in line with FactSet’s estimate of $1.08 but missed Morningstar strategist Eric Compton’s forecast of $1.26. He says he expects to see a decline in the Zions’ annual net interest income after the bank reduced its expectations, but he adds that Zions is positioned to earn decent adjusted returns on tangible equity and is building capital.
Although KeyCorp missed expectations for net income and revenue in the second quarter, the bank deposits grew $1 billion by quarter-end. “Expenses were down nearly 9% from the prior quarter, and stable compared to last year,” KeyCorp CEO Chris Gorman says.
"We remain focused on improving productivity and efficiency across our business."
Financial-services stocks such as Northern Trust [NTRS] and Charles Schwab [SCHW] also rose after posting their second-quarter results.
Northern Trust’s revenue was in line with the FactSet estimate while its earnings per share was a miss. The firm expects its third quarter to have a decline of 5% in net interest income, which Morningstar equity analyst Rajiv Bhatia says is "not as bad as the market feared" following second-quarter results from State Street [STT]. Northern Trust also showed improvement in managing its expenses, with adjusted expenses down to 115% from 120% in the first quarter.
Charles Schwab’s revenue of $4.66 billion and earnings per share of $0.75 beat analysts’ estimates. Morningstar sector director Michael Wong highlights that the financial-services company’s increased “clarity on additional expense savings and signs that the company may be past the peak of high-cost funding usage” are positive news for traders.
Which Stocks Are Down Right Now?
Shares for the International Group of Companies IPG fell after the advertising agency slashed growth expectations for the year by half. CEO Philippe Krakowsky attributes the "puts-and-takes on revenue" to significant weight from the technology sector.
"In addition, modestly heightened macro uncertainty impacted certain of our specialty assets and traditional consumer agencies," he adds.
Toast [TOST] stock fell after the restaurant software provider announced it would roll back its $0.99 fee on digital orders. The move came amid complaints from the company’s small-restaurant customer base, which drew investigative interest from the U.S. House Committee on Small Business.
Morningstar equity analyst Sean Dunlop says the rollback makes sense, given that most online ordering platforms have higher transaction fees. However, "both customers and restaurants felt blindsided by the fee change, with partner restaurants scrambling in many cases to offer offsetting coupons and with a handful of operators going so far as to look into alternative [point-of-sale] providers," he adds.
Shares for Discovery Financial Services [DFS] dropped after announcing it overcharged merchants who accepted its credit cards by misclassifying certain accounts. The firm says that the affected amount of revenue involves less than 1% of cumulative transaction fees since 2007. Discovery has reserved $365 million to compensate those affected and will review its corporate governance and compliance policies.
Equifax [EFX] stock fell after the credit reporting agency cut its full-year earnings per share guidance by $0.25. Equifax chief executive Mark Begor says he expects the subpar June performance of the U.S. mortgage market to continue, adding that the adjustment reflects "the more negative impact of the weaker mortgage market and loss of high margin mortgage revenue."
Albemarle [ALB] stock declined after the chemical manufacturer announced changes in its agreement with Mineral Resources. The Australia-based mining company backed out a deal to acquire a stake in Albemarle’s lithium processing facilities in China. MinRes will instead pursue plans to build its own processing plant, while Albemarle will retain full ownership of its China-based plants.