This article was originally published by Morningstar Australia. The views expressed in it are those of the individual participants and not of Morningstar itself
It’s been a busy year for chart makers. New case numbers bombard our screens daily. Rising inflation is forcing Y-axes around the world to reach levels that have not been seen in decades . To commemorate the year end, we asked Morningstar editorial team members to pick out their favourite charts from 2021--the interesting, the weird and the unexpected.
Today’s ten charts bring new twists to some of the year’s biggest stories, from the impact of age on inflation to Covid-19's effect on influenza. They also highlight stories drowned out by the drumbeat of the virus itself, like the curious case of the Australian family home.
Stopped in Our Tracks
As laboratories scrambled to test vaccines back in 2020, policy makers were running their own experiments.
Offices shuttered and workers were sent home as governments hit pause on their economies. The collapse in economic activity in the UK was unprecedented, says Morningstar UK editor, Ollie Smith:
“It’s a stark reminder of just how catastrophic coronavirus was for the UK economy," he says.
"We shouldn’t be deceived by short-term 'bounce-back' projects. The whole affair is, in GDP terms at least, unlike anything at occurred during the Great Financial Crisis of 2008.”
Covid Reduced Influenza Cases
That experiment triggered unintended consequences across the globe: air pollution plummeted as engines went silent; a rush for toasters and TVs by home-bound populations shocked global supply chains.
Of them all, the disappearance of influenza stuck with Morningstar equity analyst Angus Hewitt. The disease normally notches more than a hundred thousand cases annually but anti-covid measures cut that to near zero.
“Who would’ve guessed? Measures to contain a highly contagious respiratory disease contained a highly contagious respiratory disease,” Hewitt says, with more than a passing glance at the anti-lockdown camp.
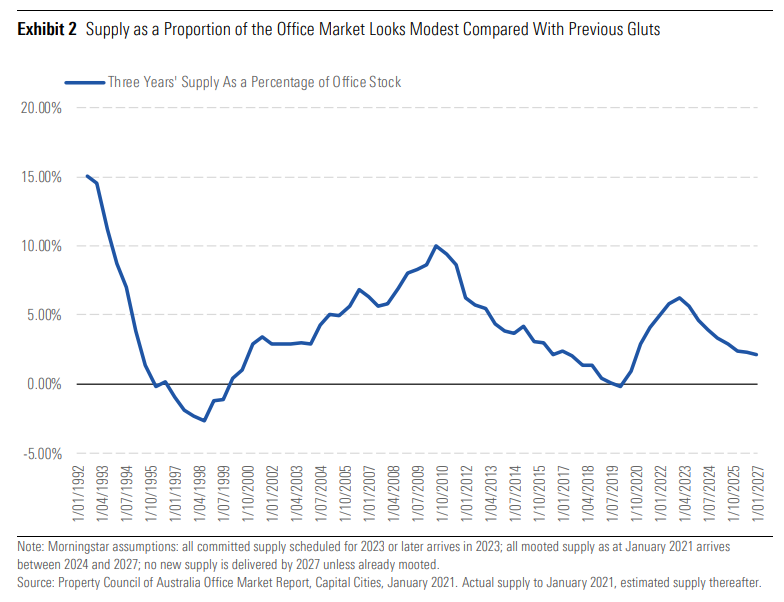
The Office Ain't Dead (Yet)
Covid-19 hit commercial real estate hard. New buildings stood vacant as companies sent employees home. The move to remote working sparked claims that the end of the office was nigh--and with it commuting and shared workspaces.
Not so, says Morningstar senior equity analyst Alex Prineas. His favorite chart this year shows how the supply glut remains small by historical standards. In Australia, at least, tenants continued to snap up floor space in 2021, with sales just short of the records notched in 2019. Expect the office to stick around for years to come.
Complicated Coal
2021 was a complicated year for fossil fuel investors. Renewed commitments to cut emissions at the COP26 climate conference came as soaring fuel prices delivered mega-returns for the energy sector.
Coal typifies this unusual situation, says Morningstar director of equity research Mathew Hodge. Even as banks cut back lending due to ESG concerns, coal miners like Whitehaven Coal were up more than 50% year to date thanks to the highest prices in a decade.
“It goes to show that with ESG becoming a bigger focus for governments, companies and investors, not all of the outcomes will be intuitive,” Hodge says.
However, high dividends tend to come with environmental, social and governance risks, as this chart from Morningstar data journalist Lauren Solberg shows.
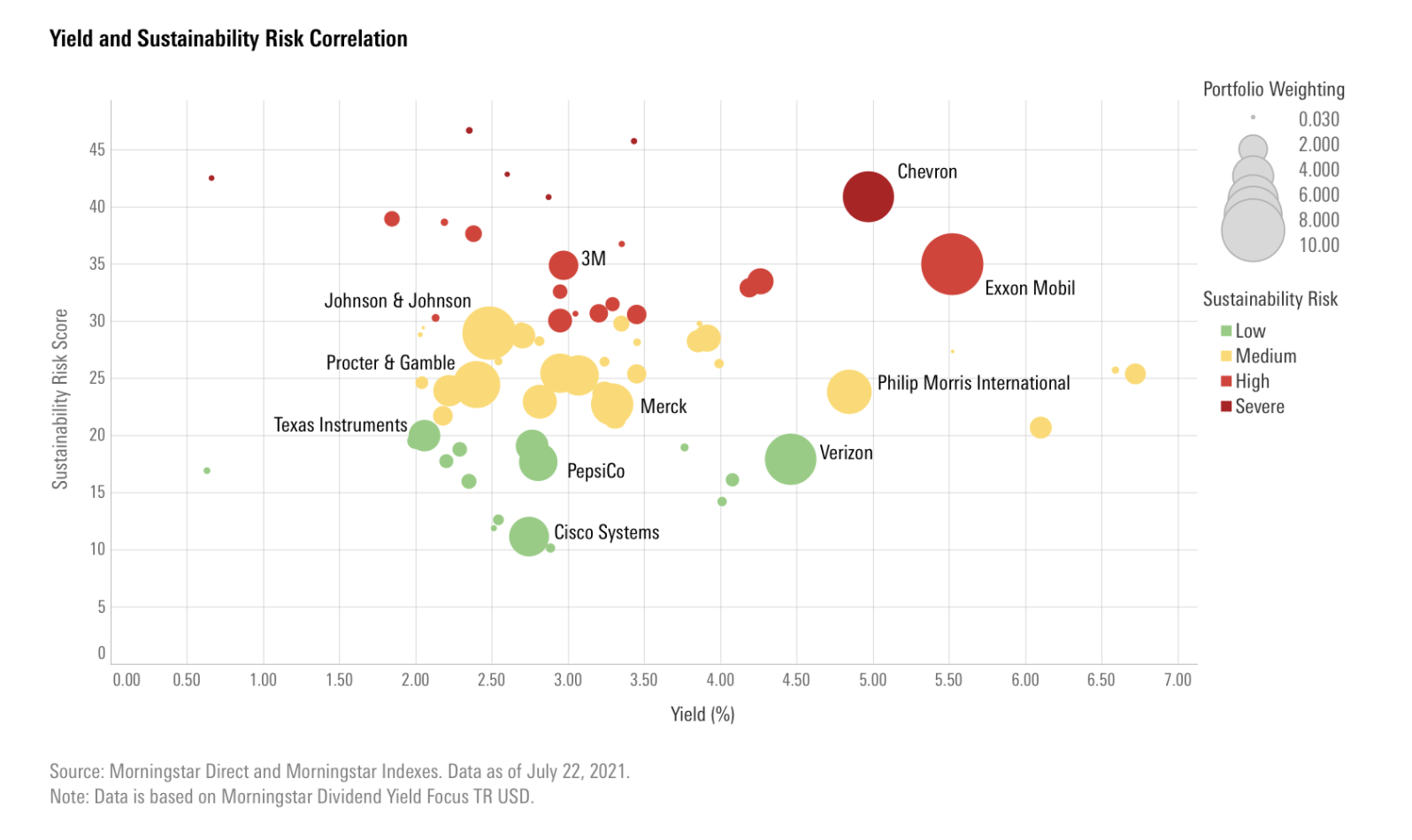
In the US, dividends and ESG risk intersect in the oil giants Chevron and Exxon. Meanwhile, companies like Rio Tinto, where chief executive Jean-Sebastien Jacques stepped down last year amid a scandal over the miner's destruction of sacred indigenous sites in Western Australia, prove the continuing presence of moral hazard in the energy sector.
Beware Inflation
Morningstar editorial director Sheryl Rowling, editorial manager Emma Rapaport, and I too, all agree that, if you weren't careful, examining inflation data could have taken up a lot of your time this year.
Behind the headline inflation number are thousands of individual prices. This chart divides those into the major categories. The case for US inflation fading rests on the double digit jumps in cars, hotels and gasoline fading in the new year.
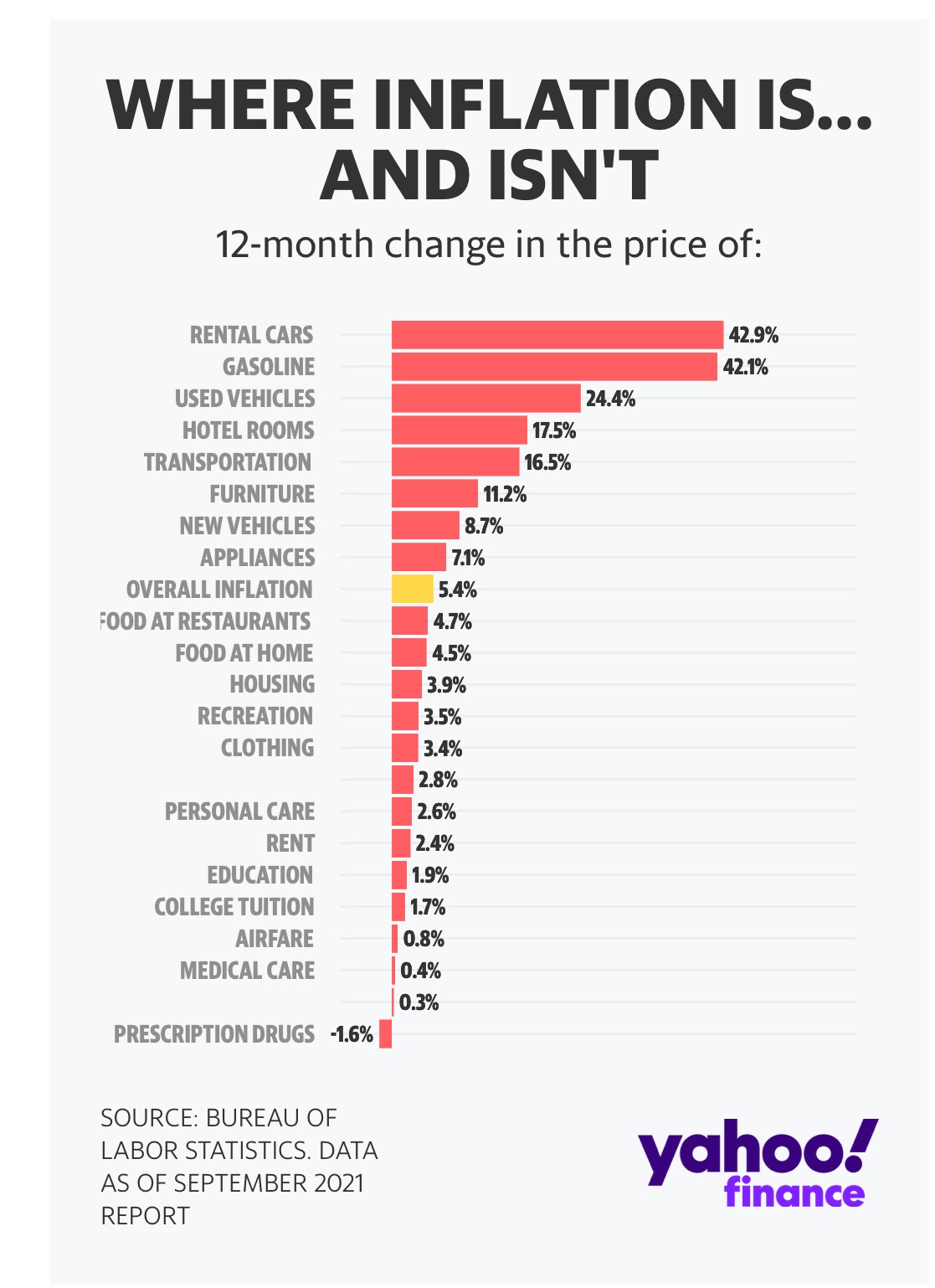
Emma’s favourite chart put rising prices into a generational context. Published in The New York Times, it shows why the lived experience of younger investors may make them more sanguine about today’s inflation than their parents or grandparents.
For me, though, it's all about the Federal Reserve. Few changes this year have been as dramatic as the about-face at the US central bank.
When the bank's decision making committee met this March, most members forecast rates to remain near zero into 2022. Fast forward nine months and three rate hikes are now expected next year.
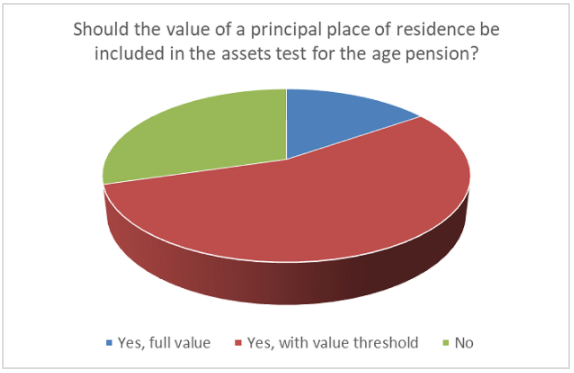
Aussies Back Cuts to Pension Benefits For Wealthy
The family home occupies a special place in the Australian psyche, so editorial director Graham Hand was surprised to find so many people were willing to include it in the age pension asset test.
Doing so would cut benefits to pensioners in multi-million-dollar homes. It's a good thing too, as he argued in his article: ‘10 reasons wealthy Australians shouldn’t receive welfare’.
“I thought it was not such a mainstream subject and would garner a limited response, but it was the biggest article of the year. It was one of those that really hit a nerve," he says.
A debate about means testing pensioner benefits in the UK has been simmering in the UK since the resignation of Iain Duncan-Smith in 2016. Could 2022 be the year policy makers finally have to bite the bullet?
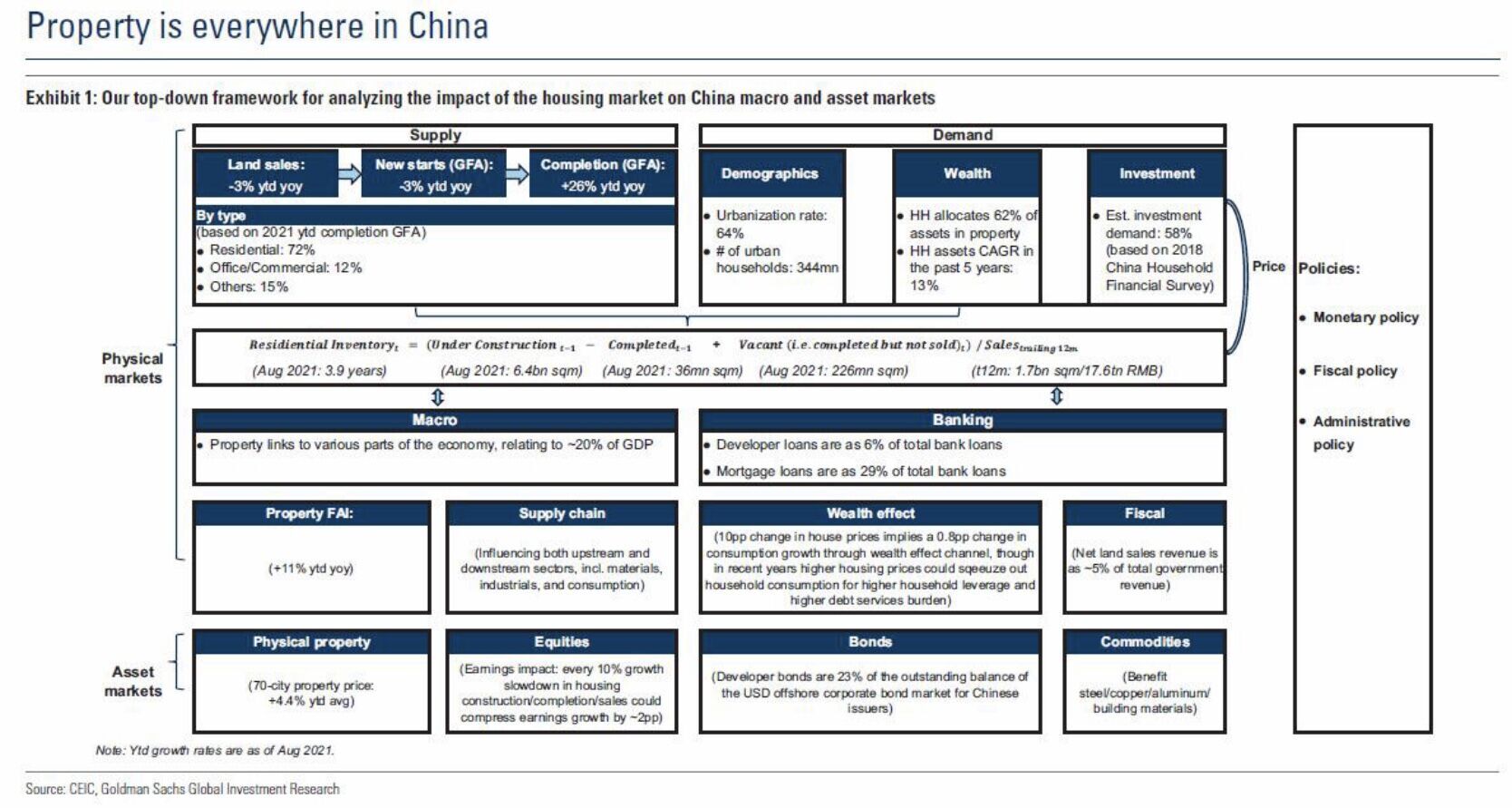
Chinese Property And The World
From Hong Kong, data journalist Kate Lin shares a chart from Goldman Sachs showing the myriad ways Chinese real estate impacts the world.
The debt crisis at Evergrande put the sector under the spotlight this year but the impact extends far beyond any one developer. Real estate is implicated in 20% of China's GDP, while a third of its loans are to developers or buyers.
Then there's the international spillovers. Chinese property consumes roughly a fifth of global steel and copper. Property developers issued a quarter of China’s offshore US dollar bonds.